Autocad Find Block Location in Drawing
Introduction
In the comments section of the previous post about AutoCAD and Excel interaction, a blog reader (Tim) asked me if it is possible to insert blocks in AutoCAD from Excel. I gave him some insight and I think that it's time to present the complete solution, which involves AutoCAD's InsertBlock method. The code presented today is not new; it was written actually some months ago (in April). Anyway, according to AutoCAD VBA help, the structure of InsertBlock method is the following:
RetVal = object.InsertBlock(InsertionPoint, BlockName, Xscale, Yscale, Zscale, RotationAngle)
Main parameters:
RetVal: Block Reference object. The placed block as a Block Reference object.
Object: ModelSpace Collection, PaperSpace Collection, Block – the objects this method applies to.
InsertionPoint: Variant (three-element array of doubles); input-only. The 3D WCS coordinates specifying the location in the drawing to insert the block.
BlockName: String; input-only. The name of the AutoCAD drawing file or the name of the block to insert. If it is a file name, include the .dwg extension and any path information necessary for AutoCAD to find the file.
Additional optional parameters:
Xscale: Double; input-only (optional). The default value is 1 (must be >0).
Yscale: Double; input-only (optional). The default value is 1 (must be >0).
Zscale: Double; input-only (optional). The default value is 1 (must be >0).
RotationAngle: Double; input-only (optional). The rotation angle relative to the WCS X-axis expressed in radians. The default value is 0.
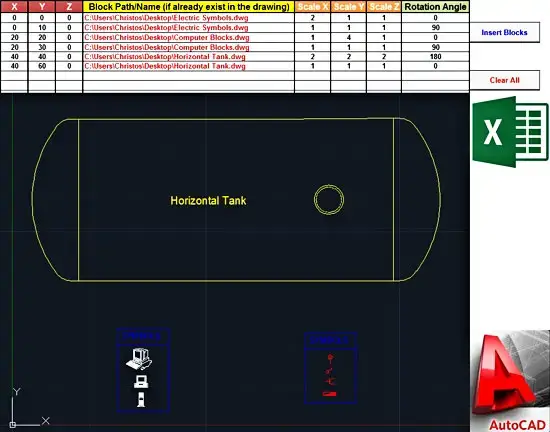
The sample workbook that you will find in the Downloads section below requires two main and two optional parameters: the coordinates of the insertion point (in X, Y, Z) and the block name (or its full path, including the .dwg extension). Optional parameters are the scale factors (in X, Y, and Z axes) as well as the rotation angle. Then, by clicking the "Insert Blocks" button the blocks are inserted either in the active drawing (if AutoCAD is already launched), or in a newly created drawing.
VBA code for adding blocks in AutoCAD from Excel
The code is actually a loop; most of the code is used to initialize the AutoCAD object, as well as the active/new drawing. Note that the InsertBlock method here is used with a small variation: the RotationAngle must be given in degrees. The conversion – degrees to radians – is being done internally.
Option Explicit 'A custom type that holds the scale factors of the block. Private Type ScaleFactor X As Double Y As Double Z As Double End Type Sub InsertBlocks() '-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 'Inserts blocks in AutoCAD using data - insertion point, block name/full path, scale factors, rotation angle - from Excel. 'Note that the block name or the block path must already exists, otherwise nothing will be inserted. 'The code uses late binding, so no reference to external AutoCAD (type) library is required. 'It goes without saying that AutoCAD must be installed at your computer before running this code. 'Written by: Christos Samaras 'Date: 21/04/2014 'e-mail: [email protected] 'site: http://www.myengineeringworld.net '-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 'Declaring the necessary variables. Dim acadApp As Object Dim acadDoc As Object Dim acadBlock As Object Dim LastRow As Long Dim i As Long Dim InsertionPoint(0 To 2) As Double Dim BlockName As String Dim BlockScale As ScaleFactor Dim RotationAngle As Double 'Activate the coordinates sheet and find the last row. With Sheets("Coordinates") .Activate LastRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row End With 'Check if there are coordinates for at least one circle. If LastRow < 2 Then MsgBox "There are no coordinates for the insertion point!", vbCritical, "Insertion Point Error" Exit Sub End If 'Check if AutoCAD application is open. If is not opened create a new instance and make it visible. On Error Resume Next Set acadApp = GetObject(, "AutoCAD.Application") If acadApp Is Nothing Then Set acadApp = CreateObject("AutoCAD.Application") acadApp.Visible = True End If 'Check (again) if there is an AutoCAD object. If acadApp Is Nothing Then MsgBox "Sorry, it was impossible to start AutoCAD!", vbCritical, "AutoCAD Error" Exit Sub End If On Error GoTo 0 'If there is no active drawing create a new one. On Error Resume Next Set acadDoc = acadApp.ActiveDocument If acadDoc Is Nothing Then Set acadDoc = acadApp.Documents.Add End If On Error GoTo 0 'Check if the active space is paper space and change it to model space. If acadDoc.ActiveSpace = 0 Then '0 = acPaperSpace in early binding acadDoc.ActiveSpace = 1 '1 = acModelSpace in early binding End If On Error Resume Next 'Loop through all the rows and add the corresponding blocks in AutoCAD. With Sheets("Coordinates") For i = 2 To LastRow 'Set the block name. BlockName = .Range("D" & i).Value 'If the block name is not empty, insert the block. If BlockName <> vbNullString Then 'Set the insertion point. InsertionPoint(0) = .Range("A" & i).Value InsertionPoint(1) = .Range("B" & i).Value InsertionPoint(2) = .Range("C" & i).Value 'Initialize the optional parameters. BlockScale.X = 1 BlockScale.Y = 1 BlockScale.Z = 1 RotationAngle = 0 'Set the optional parameters (if there are values on the corresponding ranges). If .Range("E" & i).Value <> vbNullString Then BlockScale.X = .Range("E" & i).Value If .Range("F" & i).Value <> vbNullString Then BlockScale.Y = .Range("F" & i).Value If .Range("G" & i).Value <> vbNullString Then BlockScale.Z = .Range("G" & i).Value If .Range("H" & i).Value <> vbNullString Then RotationAngle = .Range("H" & i).Value 'Add the block using the sheet data (insertion point, block name, scale factors and rotation angle). 'The 0.0174532925 is to convert degrees into radians. Set acadBlock = acadDoc.ModelSpace.InsertBlock(InsertionPoint, BlockName, _ BlockScale.X, BlockScale.Y, BlockScale.Z, RotationAngle * 0.0174532925) End If Next i End With 'Zoom in to the drawing area. acadApp.ZoomExtents 'Release the objects. Set acadBlock = Nothing Set acadDoc = Nothing Set acadApp = Nothing 'Inform the user about the process. MsgBox "The blocks were successfully inserted in AutoCAD!", vbInformation, "Finished" End Sub One thing that should be highlighted is that when inserting a block from a .dwg file, the results might not be as expected. The reason is that by default, AutoCAD uses the coordinate (0, 0, 0) as the base point when inserting a drawing file. You can change the default coordinate by following the next 4 steps:
- Open the dwg file you want to use as a block.
- Type INSBASE at the command line.
- Specify with your mouse a new point that you want to use as a base point.
- Save the file.
That's all; AutoCAD will use the new base point the next time you insert the drawing.
Note that if you have AutoCAD 2010 or a newer version, you will have to download and install the VBA module, otherwise the code will probably fail.
- AutoCAD 2010 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2010 VBA module 64-bit
- AutoCAD 2011 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2011 VBA module 64-bit
- AutoCAD 2012 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2012 VBA module 64-bit
- AutoCAD 2013 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2013 VBA module 64-bit
- AutoCAD 2014 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2014 VBA module 64-bit
- AutoCAD 2015 VBA module 32-bit
- AutoCAD 2015 VBA module 64-bit
All links were copied from Autodesk's website.
Downloads

The zip file contains an Excel workbook along with 3 sample AutoCAD drawings that can be used as blocks. In these sample drawings, the INSBASE command has been used to change the default base point (as described above). The workbook can be opened with Excel 2007 or newer. Please enable macros before using it.
Read also
Counting Existing Blocks In AutoCAD (VBA Add-In)
Drawing Points In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Drawing Circles In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Add Text In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Add Dimensions In AutoCAD Using Excel & VBA
Send AutoCAD Commands From Excel & VBA
Page last modified: October 1, 2021
Source: https://myengineeringworld.net/2014/07/insert-blocks-autocad-excel-vba.html
0 Response to "Autocad Find Block Location in Drawing"
Post a Comment